HCatalog Architecture
HCatalog is a table and storage management layer designed for Hadoop. It allows users working with various data processing tools, such as Pig and MapReduce, to more easily read and write data across the grid. HCatalog provides a table abstraction that offers users a relational view of data stored in the Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS), ensuring they do not have to worry about the location or format of their data—whether it's in RCFile format, text files, SequenceFiles, or ORC files.
HCatalog supports reading and writing files in any format for which a SerDe (serializer-deserializer) can be created. By default, it supports RCFile, CSV, JSON, SequenceFile, and ORC file formats. To use a custom format, we must provide the corresponding InputFormat, OutputFormat, and SerDe.
Architecture -
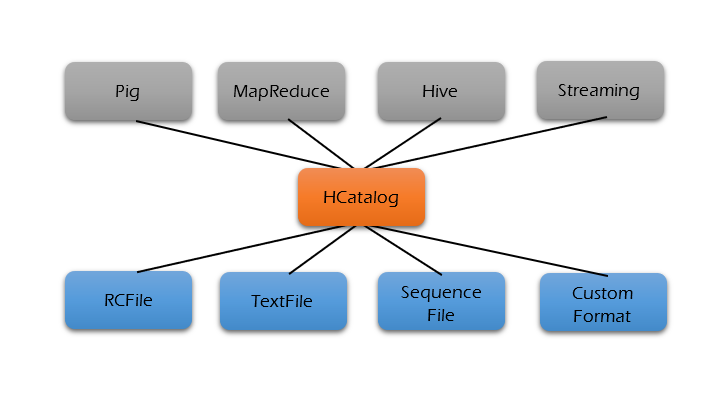
HCatalog is built on top of the Hive metastore and incorporates Hive's DDL. It provides read and write interfaces for Pig and MapReduce, using Hive's command line interface (CLI) to issue data definition and metadata exploration commands.
Interfaces -
- The HCatalog interface for Pig includes two main components: HCatLoader and HCatStorer. HCatLoader is used to read data from a specified table. You can specify which partitions to scan by adding a partition filter immediately after the load statement. On the other hand, HCatStorer is used to write data to a given table, and you can optionally specify partition keys if you want to create a new partition.
- The HCatalog interface for MapReduce, which includes HCatInputFormat and HCatOutputFormat. HCatInputFormat lets you choose a table to read data from. You can also specify which parts of the table you want to look at by using a selection filter. HCatOutputFormat allows you to write data to a table and lets you create new parts in the table if needed. You can write to a specific part by giving the partition keys and their values when you use the setOutput method.
- There is no specific interface for Hive. Since HCatalog uses Hive’s metastore, Hive can directly read data from HCatalog.
Data Model -
- HCatalog provides a relational view of data.
- Data is organized into tables, which can be stored in databases. These tables can also be hash-partitioned based on one or more keys. This means that for each specific value of a key (or a combination of keys), there will be one partition that contains all the rows associated with that value (or set of values).
- New partitions can be added to a table, and existing partitions can be removed.
- When a partitioned table is created, it does not have any partitions initially. In contrast, unpartitioned tables essentially have a single default partition that must be set up at the time of creation.
- Partitions contain records. Once you create a partition, you cannot add, remove, or update records in it. Partitions are multi-dimensional, not hierarchical.
- Records are organized into columns, which have names and data types.
- HCatalog uses the same data types as Hive.
