Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) | TutorialsCampus
What is SDLC?
SDLC stands for Software Development Life Cycle and also called as Application Development Life Cycle. SDLC is a well-organized model or process or framework for technical and non-technical activities to develop and deliver a high quality system that meets or exceeds the business or customer requirements.
To be precise, SDLC aims to develop the high quality system that statisfies or exceeds the customer expectations, works efficiently and effectively in the planned environment, have less maintain cost and cost-efficient to enhance the product.
The main objective of SDLC is to meet/exceeds the customer expectations with a maximum possibility of high quality. The development process should be completed within the given budget and timelines.
Detailed information -
SDLC is originally begins as "System Development Life Cycle" in 1960s. Initially "Geoffrey Elliott" explains it for large organizatons to manage the complex business requirement that requires a lot of analysis and processing. Overtime, process has been adopted by all scaled organizations for hardware and software development.
Traditional system-development life cycle consists of five stages. That are now increased to seven phases. The increased steps helping the analysts to define the clear goals to achieve the specific targets.
SDLC uses systematic approach to define and describe the process similar to project life cycle (PLC). The SDLC process used and followed when there is an IT or IS project under development.
SDLC is applicable to a wide range of software and/or hardware applications where systems are made up of sofware alone, of hardware alone, or even the combination of both hardware and hardware.
SDLC methodology is used by almost all organizations from smaller to larger.
Each phase of SDLC has its own importance and the output of each phase would be the input for next phase.
Why SDLC?
The business organizations or companies that are not in software also depend on the software and technology to do their business. Those orgranizations or companies should adop of some solution to pull software align and optimize to their business requirements. So the prople other than developers or engineers should understood the concept of SDLC approach to get insync with the remaning prople that are insync with developers and engineers. The people beyond the developers or engineers are almost all people in the industry who are using software solutions.
There are many reasons to follow SDLC and let us see each one of them in detail below -
- It is believed to be a systematic and effective procedure to develop a system efficiently and effectively.
- Provides a platform for project planning, scheduling and estimation.
- Provides transparency on the planning to its stakeholders.
- Helps to track and control the project activities.
- Provides framework to group the activities and deliverables.
- Helps to reduce risk of project.
- Helps to manage the project further.
- Helps to increase and improve the development speed.
Process -
SDLC process has a series of phases that are using in software development to develop and deliver a high quality product. SDLC phases covers the complete lifecycle of the software product from its inception to the maintanence.
SDLC process lowers the cost of software development and parallelly improves the quality and reduces the effort or time. It removes the pitfalls of software development in all the phases. THe plan actually starts from analysis if it is a new system design or evluating system for deficiencies if it is an existing system. SDLC process eliminates the redundant rework by taking end-user or client feedback.
SDLC process has a strong focus on testing phase to produce the high quality product. For example, most of organizations believes that having more focus on the testing can save rework, time and money.
Phases -
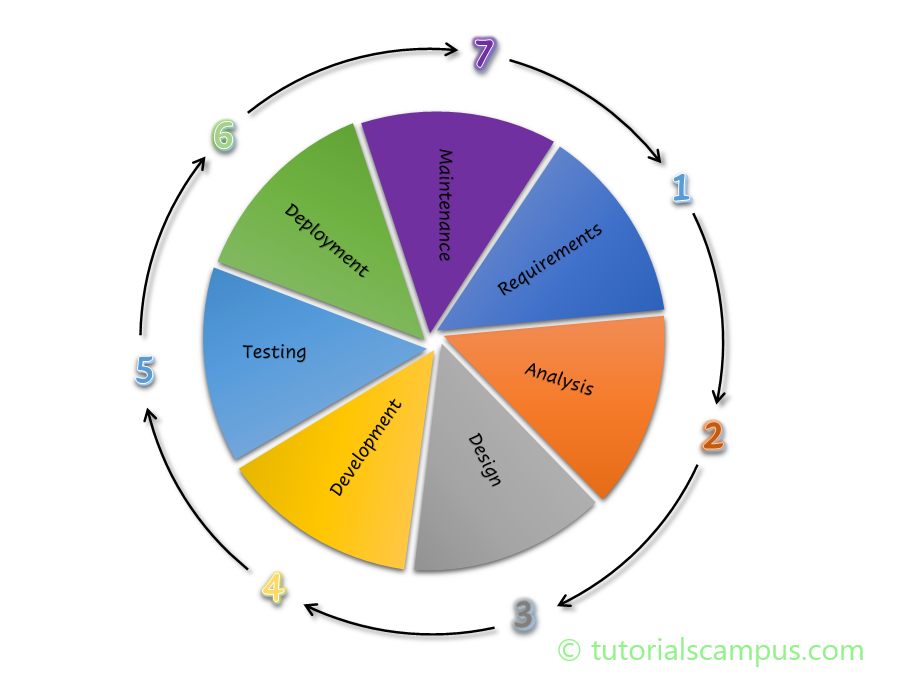
Software Development life Cycle (SDLC) seven predefined phases are -
- Planning & Requirement Phase.
- Analysis Phase.
- Design Phase.
- Development or Implementation Phase.
- Testing Phase.
- Deployment Phase.
- Maintenance Phase.
It is always a best practice or more important to follow the order of phases to avoid pitfalls and develop the product in systematic manner.
For example, if the phases are not followed in the predefined order, there will be no control on when to start phases. i.e. development may start without a proper design. Design, development, testing may start without a proper planning. These may lead to the rework in all areas which leads to a project failure.
Below diagram represents the pictorial representation of each phase and the predefined order of them.
Planning and Requirements Phase -
Planning is the first and foremost phase in SDLC. The senior members of the project like Manager, Delivery Manager, Domain Experts, Sales Managers etc involves in this phase. At the first step, the requirement idea and the inputs explains the overview of the estimates to everyone. Based on the inputs, the project execution approach, model used to develop the system would be decided. It also helps to do feasibility study economic and other operational aspects. In this, the overall project planning, resource planning, risk identification and overall project execution planning discussed and finalized. Risk identifying is generally done in this phase. A feasibility study is conducted on the Technical aspects which help to decide and describe the approach which could be followed to implement the project successfully with a low risk.
Requirement Gathering is the most important and first phase of SDLC. In this phase, business analyst and project manager participate in the meetings with client to gather the requirements.
- Client is the owner of the product and provides the information about what to build, who will use it or purpose of it to all the participants.
- Business analyst is the person who gathers the high level requirements from the client and document them in the form of business requirements
- Project Manager can located at onshore/offshore who is going to handle the project.
- Input - New requirement or idea or issue to improve the business.
- Outcome - Business requirements/BRS.
- Who invloves - Client, Business Analyst, Project Manager and all Stake holders.
Business requirements are generally documented in Business Requirement Document (BRS). Note that the BRS document name may gets changed based on the naming conventions defined in the project and name varies from project to project.
Examples - Business Specification (BS), Customer Requirement Specification (CRS), etc, and many more.
Analysis Phase -
Once the requirements gathering phase completed, Business Analyst (BA) converts the business requirements into technical requirements with the help from senior team members like SMEs (Subject-matter experts) and team leads. The technical requirements documented in a document called SRS (Software Requirement Specification) document. SRS consists of all the technical requirements for all system involved (that includes cross-applications if exists). SRS document should send for approval from the client or SMEs from client side to proceed with the next phases.
Note that SRS document name varies from project to project based on the naming standard defined. Examples - Requirement Specification Document (RSD), Project Specification Document (PSD), etc, and many more.
- Input - Business requirements/BRS.
- Outcome - Technical requirements/SRS.
- Who invloves - BA and senior team members like SMEs (Subject-matter experts) and team leads.
Design Phase -
Design phase turns the requirements from SRS into a design plan called the Design Document Specification (DDS). Developers takes the requirements from SRS and creates their rough designs, working models, specifies how the software works, how the new design looks, how the control flow from screen to screen etc,. Design phase also models the design that includes - architecture, user interface, platforms, programming, communications and security etc,. In another words, overall system architecture is designed by defining their functionality of each module that includes their interaction with cross-systems.
The Design Document Specifications that are two types based on their level of design. Those are -
- High-level Design (HLD) - HLD contains the high-level architecture changes or design changes. Senior developers or architects creates HLD.
- Low-level Design (LLD) - LLD constans very detailed level architecture or design changes. Senior developers or developers creates LLD.
These two documents contain only design and sometimes code as well. The architects usually provide more than one approach in a Design Document Specification. This DDS sent for review to all the stakeholders and the best approach would be selected based on the features such as robustness, budget and timing constraints.
Once the architecture is selected, the stakeholders would then propose the modules design, data flow diagrams etc.
- Input - Technical requirements/SRS.
- Outcome - Design Document Specifications (DDS).
- Who invloves - Senior team members like SMEs (Subject-matter experts) and team leads.
Development or Implementation Phase -
Once the DDS gets approved, Development phase gets started. Developers start programming with the code by following organization coding standards. Once coding completed, the programmers uses the programming tools to compile and debug the programs to verify weather new code is working or not.
Developers from all levels in the team involves in this phase. The code is documented as Source Code Document (SCD). Developers has many responsibilities in this phase namely - coding and compilation of source code to make error free.
- Input - Design Document Specifications (DDS).
- Outcome - Source Code Document (SCD) and developed product.
- Who invloves - Developement team member from all levels.
Testing Phase -
Once the coding completed, the code gets tested to check whether it is working as expected or not. The developer performs the initial testing that are unit testing (UT) and/or Application Integration Testing (AIT) before handover the code to the testing team. If everything is fine, code gets migrated to the testing environment. Testing team will perform the testing from that point. The various testings the testing team performs are - quality testing, system testing, acceptance testing and approval testing.
In this phase, testing team follows the BRS document to verify the new changes or working fine or not. If anything not working, testing team raises the defect and development team has to fix it before the specified time.
Testing team thoroughly tests for the defects by follwing the process defined in STLC (Software Testing Life Cycle) to make sure that each and every component or module is working fine.
- Input - Developed Product.
- Outcome - Defect free Product and Testing Articrafts.
- Who invloves - Developement and Testing teams.
Deployment Phase -
Once the software is fully tested and has no defects or errors, then the test results and articrafts gor reviewed by the client and provides approval for deployment. Once the software got deployed to production, then the new functionality available to the end-users who are currently using the system.
Deployement might be complex based on the system design if it is integrated with multiple systems.
- Input - Defect free Product.
- Outcome - Usable product available to end-users.
- Who invloves - Deployement Team.
Maintenance Phase –
Once the end-user starts using the newly deployed sofotware, there might be a possibility that the real-time issues starts coming up. The team has to fix these issues to avoid the loss in business if the issue has less priority or less impact. If the issue has high priority and has huge impact, client can take a decision to roll out or backout new changes and refine the functionalities as required. This process of taking care for the finished product is called as maintenance.
