Hadoop HDFS Overview
What is the distributed File System?
As data grows quickly, the amount of storage on a single machine often isn’t enough. One solution is to spread the data across multiple machines. These systems are called distributed filesystems. However, this brings challenges because the data is shared over a network.
Hadoop helps with this issue by providing a reliable filesystem. HDFS (Hadoop Distributed File System) is specifically designed to store very large files and allows access to data in a stream-like manner. It can operate on standard, low-cost hardware. Let's discuss on the terms:
- Extremely large files: - Considering the files having data in the range of petabytes (1000 TB).
- Streaming Data Access Pattern: - HDFS is designed based on the principle of writing data once and reading it many times. Once data is written, large portions of the dataset can be processed repeatedly.
- Commodity hardware: - This term refers to inexpensive hardware that is easily available in the market. This characteristic is a key feature that sets HDFS apart from other file systems.
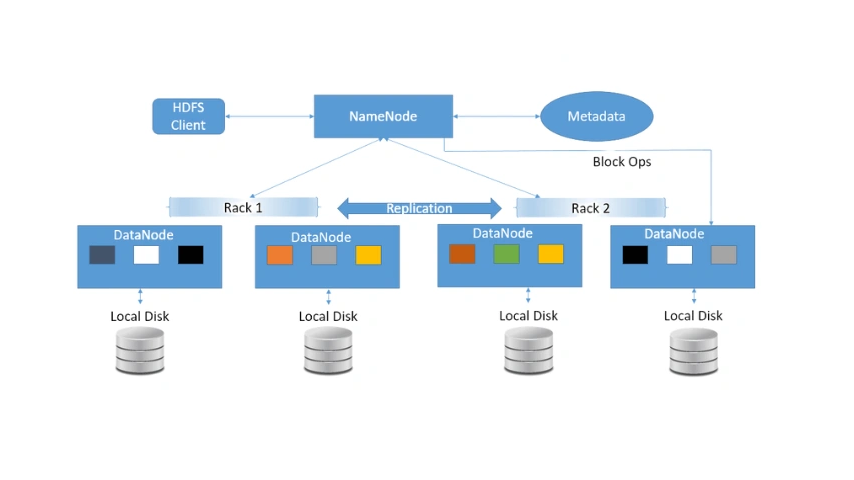
The HDFS cluster is typically made up of master-slave nodes. Those are -
NameNode(MasterNode):
- Manages all the slave nodes and assigns tasks to them.
- Executes filesystem namespace operations, such as opening, closing, and renaming files and directories.
- Should be deployed on reliable, high-configuration hardware rather than commodity hardware.
- Runs as a master node.
- Stores metadata (data about data) like file paths, number of blocks, block IDs, etc.
- Requires a significant amount of RAM.
- Keeps metadata in RAM for fast retrieval, which helps reduce seek time. However, a persistent copy is also maintained on disk.
DataNode(SlaveNode):
- These are the actual worker nodes that perform tasks such as reading, writing, and processing data.
- They handle operations like creation, deletion, and replication upon receiving instructions from the master.
- Can be deployed on commodity hardware.
- Run as slave nodes.
- Require substantial memory as the actual data is stored here.
Explaining Distributed Storage with Example -
Assume that a 100TB file is inserted into the system. The master node (NameNode) first divides this file into blocks of 10TB. The default block size in Hadoop 2.x and above is 128 MB. These blocks are then distributed across different data nodes (slave nodes).
Data nodes replicate the blocks among themselves, ensuring redundancy. The master node keeps track of which data nodes contain which blocks. By default, the replication factor is set to 3, meaning that for each block, 3 replicas are created, including the original block.
To modify the replication factor, you can edit the 'hdfs-site.xml' configuration file, where you have the option to increase or decrease the replication factor as needed.
MasterNode records all information, including the location of every data node and the blocks they contain.
HDFC Terms -
- Heartbeat - This is the signal that a DataNode continuously sends to the NameNode. If the NameNode does not receive a heartbeat from a DataNode, it will consider that DataNode to be dead.
- Replication - This process is carried out by the DataNode.
- Balancing - If a DataNode fails, the blocks stored on it will also be lost, resulting in under-replicated blocks compared to the others. In this case, the master node (NameNode) will signal the DataNodes that have replicas of the lost blocks to replicate those blocks, ensuring a balanced distribution across all nodes.
HDFS Features -
- Supports extremely large files.
- Uses distributed storage and processing.
- Operates on commodity hardware.
- Focuses on optimizing throughput rather than latency.
- Accommodates high-latency data access.
- Offers streaming access to file system data.
- Processes data using numerous small files.
- Provides file authentication and permissions.
HDFS Advantages -
- HDFS can store large amount of information.
- It has a simple and robust coherency model, providing scalable and fast access to data.
- It can effectively serve a substantial number of clients by adding more machines to the cluster.
- HDFS provides streaming read access.
- HDFS used to read data stored multiple times but the data will be written to the HDFS once.
- The overhead of cashing is helps the data should simple be read from HDFS source.
- The recovery techniques will be applied very quickly.
- Processing logic close to the data rather than the data close to the processing logic.
- Hardware and operating systems portability across is heterogeneous commodity.
- High Economy by distributing data and processing across clusters of commodity personal computers.
- High Efficiency by distributing data, logic on parallel nodes to process it from where data is located.
- High Reliability by automatically maintaining multiple copies of data and automatically redeploying processing logic in the event of failures.
HDFS Disadvantages -
- HDFS does not give any reliability if that machine goes down.
- Enormous number of clients must be handled if all the client’s needs the data stored on single machine.
- Clients need to copy the data to their local machines before they can operate on it.
