Agile Estimation Techniques
What is an Estimation Technique?
Agile estimation is the process of predicting the effort needed to complete a task or user story. Unlike traditional methods that estimate in hours or days, Agile focuses on relative estimation, considering factors like complexity, risk, and uncertainty.
In Agile, an Estimation Technique is a method used by teams to estimate the size, effort, complexity, or time required to complete a task, user story, or feature.
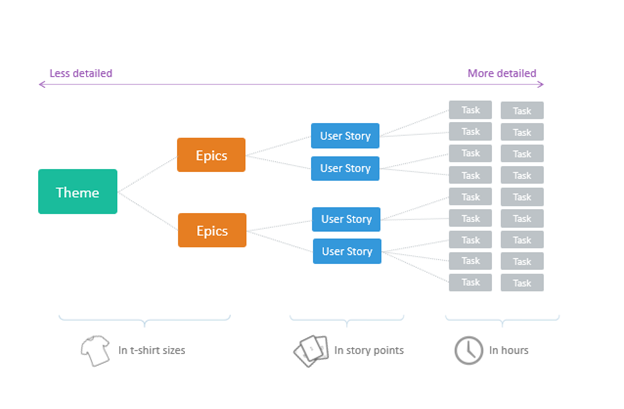
Different Estimation Techniques in Agile
Agile teams use multiple estimation techniques based on their experience, team size, and project type. Below are the most commonly used ones:
1. Story Points
Story Points are units of measure that represent the effort required to implement a user story. They consider factors like complexity, risk, and uncertainty, rather than time. The story points follow the Fibnosi series, such as 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34, 55, etc.
2. Planning Poker
Planning Poker is a consensus-based estimation technique that uses cards to assign story points to tasks. Team members use a set of numbered cards (like 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, etc.) to vote on the complexity of a story. It encourages discussion, avoids bias, and builds consensus.
How it works?
- The Product Owner explains a user story.
- Each team member secretly selects a card with their estimate.
- Everyone reveals their cards at the same time.
- If estimates vary widely, the team discusses and re-votes until they agree.
Example: Story: "User can search for hotels by city name".
- Dev A picks 2, Dev B picks 5, Dev C picks 3.
- Dev B says filtering by city might involve complex logic.
- After discussion, the team agrees on 5 story points.
3. T-Shirt Sizing
T-Shirt Sizing assigns sizes to tasks based on their relative effort. It's a quick way to categorize tasks without getting into detailed discussions. This technique uses T-shirt sizes to estimate — XS, S, M, L, XL, XXL — to represent relative effort or complexity. It is quick, high-level estimation when detailed planning isn't needed yet.
After sizing, these can be converted to story points later.
4. Affinity Estimation
Affinity Mapping involves grouping similar tasks together based on their complexity or effort. This technique helps in quickly organizing and estimating large numbers of user stories.
How it works?
- Write each user story on a card.
- Place them on a wall/board in order of effort.
- Team moves cards until they agree on relative positions.
- Assign story points based on position.
5. Three-Point Estimation
Three-Point Estimation considers three scenarios:
- Optimistic (O) – Best-case scenario.
- Pessimistic (P) – Worst-case scenario.
- Most Likely (M) – Realistic effort.
Then calculate average using formula: Estimate = (O + 4M + P) / 6
6. Bucket System Estimation
The Bucket System involves categorizing tasks into predefined "buckets" that represent different levels of effort. Team members place tasks into buckets based on their judgment, facilitating quick estimation of large backlogs.
How it works?
- Create "buckets" labeled with effort values.
- Go through user stories and assign each to a bucket.
- Refine as needed.
7. Dot Voting
Dot Voting is a prioritization technique where team members use dots to vote on tasks they believe are most important or require more effort. Each team member gets dots (votes) and places them on stories they believe are most complex.
More dots = more effort required.
