Agile SDLC
What is Agile SDLC?
Agile Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) is a flexible and collaborative approach to developing software. Instead of creating the entire product all at once, Agile divides the work into smaller, manageable segments known as "sprints," which typically last between 2 to 4 weeks. This method emphasizes adaptability and customer satisfaction by allowing for regular reassessment and adjustment of plans.
Agile Software Development Life Cycle Phases
- Concept - This is the brainstorming phase where the project's vision is established. Ideas are generated, and features are prioritized based on business value and customer needs.
- Inception - Here, the team is gathered, and initial planning takes place. Funding is secured, and basic requirements and environments are discussed to set the foundation.
- Construction Iterations - The development team works on building the product in iterations. Each iteration results in a working piece of software, incorporating feedback and evolving requirements.
- Release - Quality assurance testing is performed to ensure the product meets standards. Training and documentation are provided, and the final version of the iteration is integrated into the product.
- Production - The software is now live and requires ongoing support and maintenance. The team monitors performance and addresses any issues that arise in the live environment.
- Retirement - This phase involves ending support for outdated features or the entire product. Customers are notified, and migration plans are implemented if necessary.
The Agile Iteration Workflow
Each iteration in Agile follows a structured workflow to ensure consistent progress:
- Requirements - Define the requirements for the iteration depending on the product backlog, sprint backlog, customer, and stakeholder feedback.
- Development - Design and develop the software based on defined requirements.
- Testing - QA (Quality Assurance) testing, internal and external training, documentation development.
- Delivery - Integrate and deliver the working iteration into production.
- Feedback - Accept customer and stakeholder feedback. work on the requirements of the next iteration.
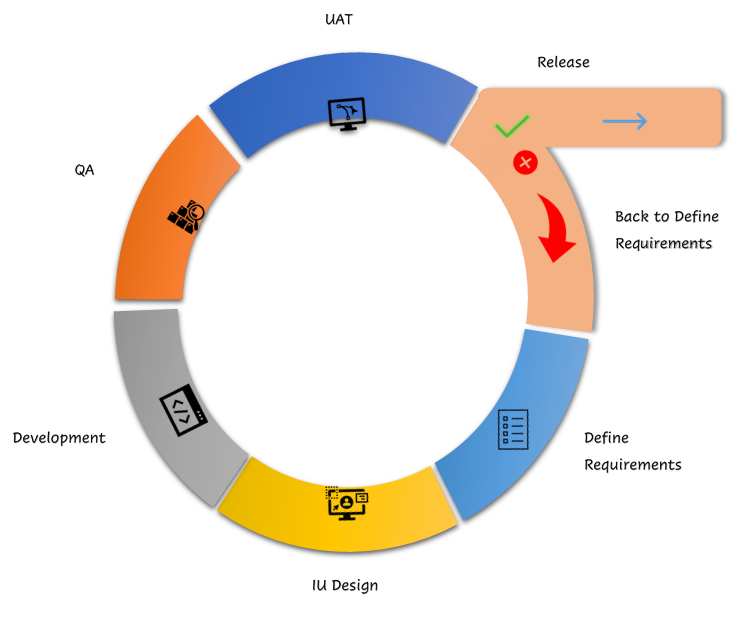
This cycle repeats, allowing the product to evolve and improve continuously.
Working with Agile Process
Agile is particularly effective for large and complex projects that require flexibility and rapid adaptation to change. To successfully implement Agile, consider the following practices:
- Daily Meetings - Host consistent or daily stand-up meetings in order to maintain open communication, hold workers accountable, and keep each iteration going forward
- Live Demonstrations - Deliver live demonstrations of each iteration's final product in order to show progress.
- Share Feedback - Receive feedback from stakeholders and customers, share it with the entire team before the next iteration begins.
- Remain Agile - Make changes to your process based on the feedback to make sure that each iteration improves the last.
