Selenium Link Text
LinkText strategy used to locate the element using the link text as in hyperlinks. There is no standard for uniqueness of the linkText on a web page and multiple elements can have same linkText. So, there is a chance that multiple links may have the same linkText. In this scenario, the first link that matches with the linkText selected for testing. linkTexts are always prefixed with the anchor tag (<a> tag) and can easily findout by using anchor tag.
Pros
- Can only select anchor elements.
- Useful when testing navigation.
Cons
- We must find the text of the link before using it.
Example
Now, let’s understand the working of linkText locator with the help of a simple example. We will launch chrome and navigate to google.com. Here, we will try to locate the gmail link using linkText locator.
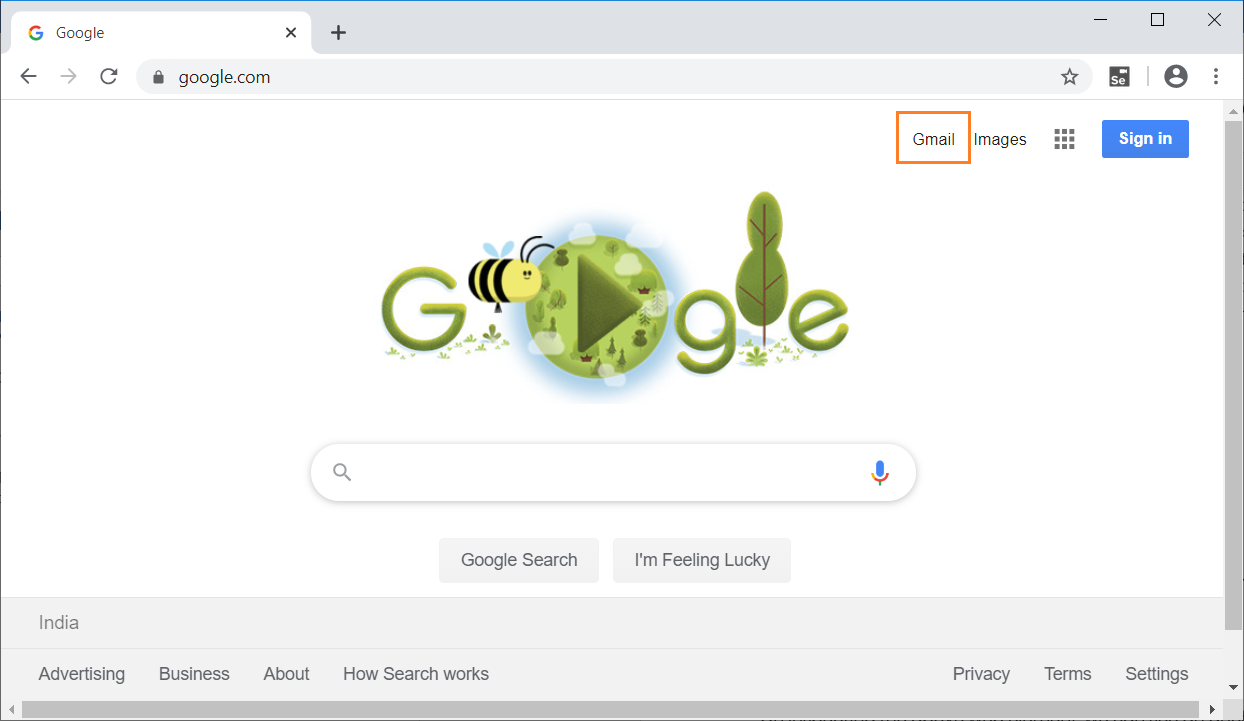
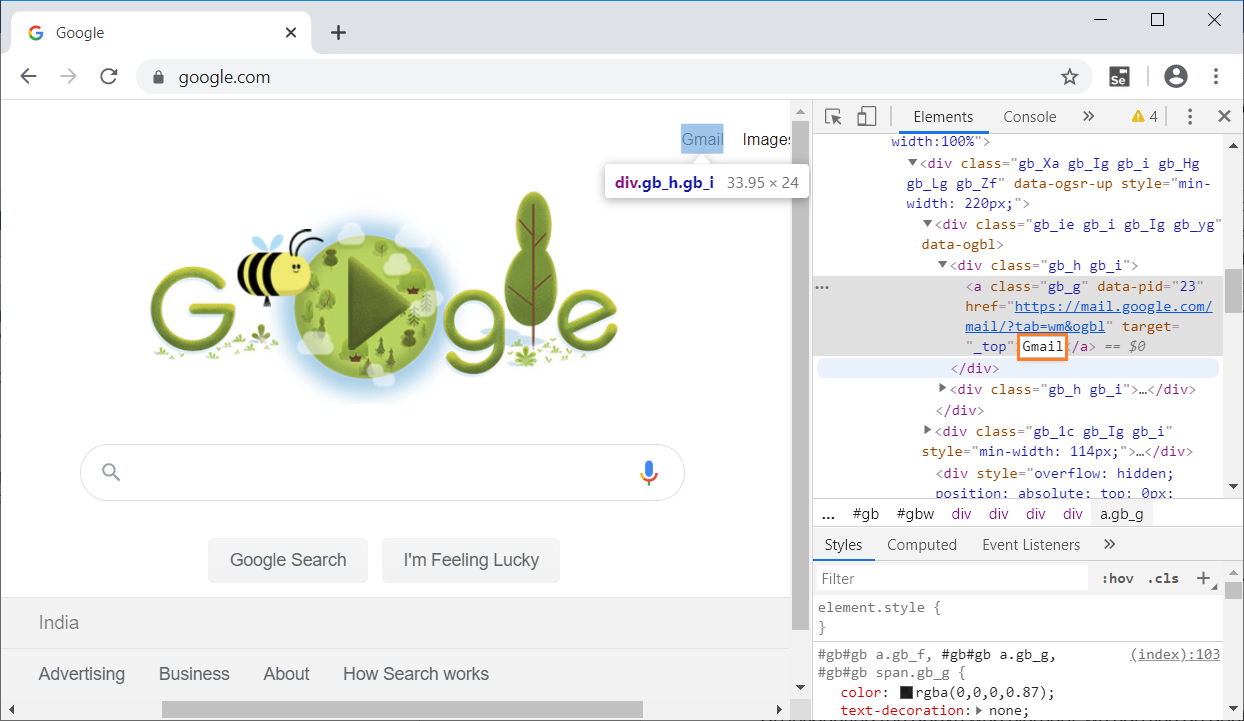
On inspecting the above web element, we can see an anchor tag (<a>) has the text Gmail. Now, we will use the value in linkText locator i.e. Gmail to open gmail login page.
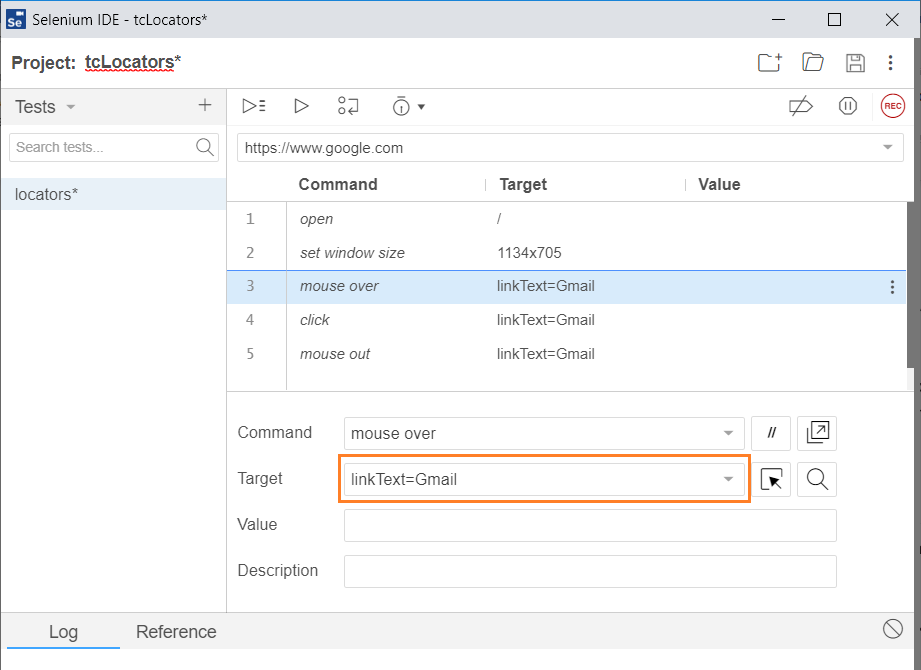
Let’s see how the automation of the search look like in Selenium IDE that navigates to gmail login page using linkText locator.
The java program for the above test is -
// Generated by Selenium IDE import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.Before; import org.junit.After;
import static org.junit.Assert.*;
import static org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.is;
import static org.hamcrest.core.IsNot.not;
import org.openqa.selenium.By;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.firefox.FirefoxDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.chrome.ChromeDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.remote.RemoteWebDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.remote.DesiredCapabilities;
import org.openqa.selenium.Dimension;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebElement;
import org.openqa.selenium.interactions.Actions;
import org.openqa.selenium.support.ui.ExpectedConditions;
import org.openqa.selenium.support.ui.WebDriverWait;
import org.openqa.selenium.JavascriptExecutor;
import org.openqa.selenium.Alert;
import org.openqa.selenium.Keys;
import java.util.*;
import java.net.MalformedURLException;
import java.net.URL;
public class LocatorsTest {
private WebDriver driver;
private Map<String, Object> vars;
JavascriptExecutor js;
@Before
public void setUp() {
driver = new ChromeDriver();
js = (JavascriptExecutor) driver;
vars = new HashMap<String, Object>();
}
@After
public void tearDown() {
driver.quit();
}
@Test
public void locators() {
driver.get("https://www.google.com/");
driver.manage().window().setSize(new Dimension(1134, 705));
{
WebElement element = driver.findElement(
By.linkText("Gmail"));
Actions builder = new Actions(driver);
builder.moveToElement(element).perform();
}
driver.findElement(By.linkText("Gmail")).click();
{
WebElement element = driver.findElement(
By.tagName("body"));
Actions builder = new Actions(driver);
builder.moveToElement(element, 0, 0).perform();
}
}
}
When you run the java program, Chrome driverlaunches chrome, redirect to google.com,clicks on the link text "Gmail" to open gmail login page.Refer the below image for the output -
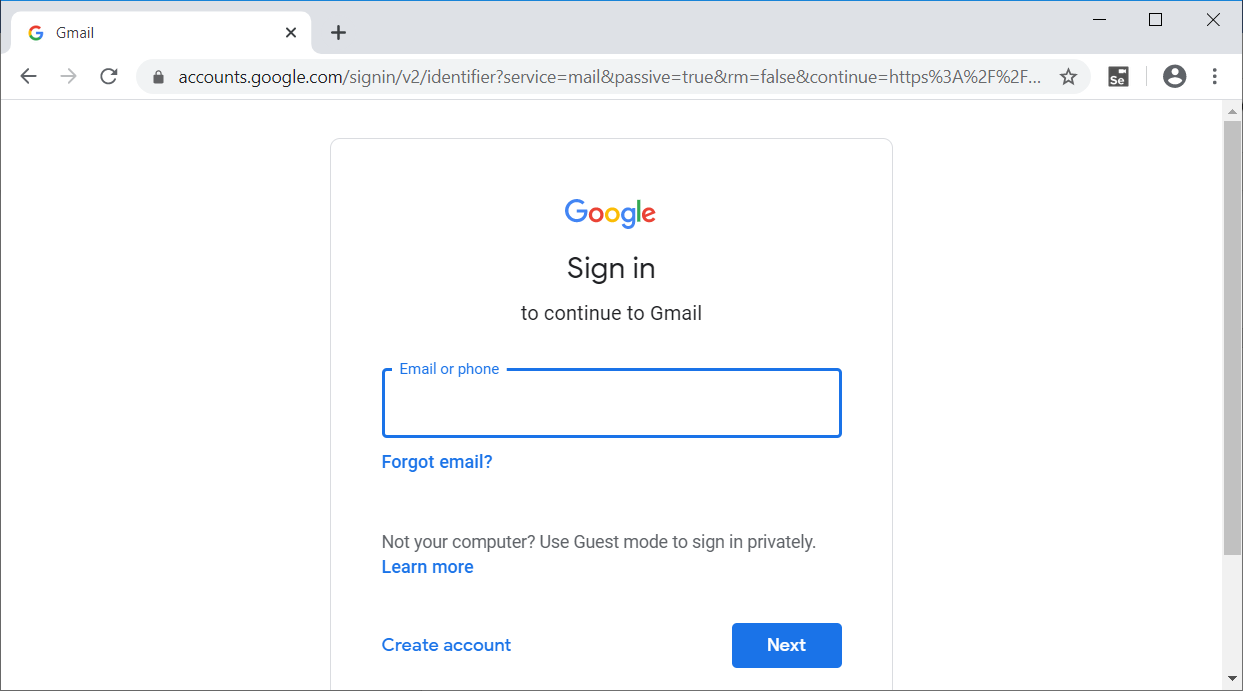
The above example gives a clear understanding of how linkText locator in Selenium works.
